RCP TEST- WATER PERMEABILITY TEST - SALT PONDING TEST
Concrete is a composite material comprising of Cement, Sand & coarse aggregate. Every material has pores, which contains voids in it. Aggregates have a more substantial void ranging from 1mm to 10mm which cement paste fills these. Even cement has voids ranging from 1micron to 10micron. Due to this interconnected and continuous link to fill one void by other material concrete is prone to permeate fluid or gases into it.Or In simple words, Presence of voids in concrete makes permeable which in turn allows water or gas to flow into it. The permeability of concrete is the ability of concrete to resist the water flow or any other substance into it when the external force is applied.
Durability of concrete is most important and complex property of concrete. If concrete is permeable, deleterious materials like water, CO2, SO2 & Cl which permeates through the pores of the concrete and reacts with the reinforcement forms rust which increases the volume of the reinforcement and damages the structure. Prior understanding of the extent and rate of permeation helps to design structure better.
Factors affecting the Concrete Permeability:
Excessive water is added to the concrete mix to increase the workability of concrete. This additional mixing of water, more than required increases the porosity in concrete and degrades the durability of concrete. To resist the entry of water into the concrete 0.4 water-cement ratio is adopted. Experiments proved that taking a water-cement ratio of 0.4 makes concrete impermeable.
Improper compaction in concrete is the major problem for porosity in concrete. Concrete should be adequately compacted using hand compaction method or machine compaction methods. Poorly compacted concrete leads to the formation of honeycomb which ultimately makes steel to corrode and forms surface cracks.
Concrete should be adequately cured by considering the atmospheric weather. Improper curing in concrete leads to the formation of cracks and in turn, it increases the permeability of concrete
Different purposes to check the Permeability of concrete
1. Measuring the Permeability of concrete as a quality control parameter: To assess and study the property of the material that we are using or going to use. Suppose we need a zero permeable concrete for construction. After investigating we found that there is a 2% of porosity, then we dismiss the concrete for construction as it is not as per specifications.
2. Evaluating the permeability of already laid concrete structure: As an engineer, we often check the Permeability property of concrete of older monuments or existing structures. This type of measuring requires a Non-destructive test as cutting concrete from the structure is not possible.
Permeability test of concrete:
This test is more important in RCC as we know that reinforcement is prone to corrosion when it reacts with the water, which in turn forms a layer around the reinforcement and causes an increase in the volume of concrete which ultimately leads to surface cracking. To resist the reinforcement to corrode, the concrete is set to permeable and Permeability test of concrete tests the same.
Not only the water or moisture there are other atmospheric deleterious materials which ingress with reinforced concrete leads to corrosion of steel.
Most commonly used tests to measure the Concrete Permeability are
2. Water Permeability by pressure
3. Ponding with a salt solution
1.Rapid Chloride Permeability test [RCP Test]
For Specifications and the quality control purposes on site, the rapid chloride permeability test [RCPT} is simple to conduct and that can be performed in a short time.
Rapid Chloride Permeability test is covered by AASHTO T 277 or ASTM C 1202 it is the test for chloride ions. As the name it proves that, this test is performed to check the Concrete’s Ability to Resist Chloride Ion Penetration.
This test is an Electrical Indication of Concrete’s Ability to Resist Chloride Ion Penetration. This test enables to predict the service life of concrete structures. It can also be used for durability-based quality control purposes.
In this test, the constant voltage (V) is applied on a concrete specimen for 6 hours and the current (i) passing through the concrete is recorded to find the coulombs.
What is coulomb?
Current is measured in amperes. A coulomb is an ampere – second;
Which means 1 ampere passed through the concrete specimen in 1 second is a 1 coulomb, and the charge passed in 60 seconds would be 60 coulombs. The more permeable the concrete, the higher the coulombs; the less porous the concrete, the lower the coulombs.
Apparatus
This test is made possible by an equipment which is known as Rapid Chloride Permeability test equipment, the test equipment consists of two reservoirs. One of them has 3.0% of NaCl solution and another reservoir has 0.3M NaOH Solution, Concrete having thickness 50mm and dia 90-100mm is used as a test specimen.
Chloride test procedure
1. The concrete specimen having dia 100mm and thickness 50mm is cast and saturated.
2. The concrete sample is placed in between the two reservoirs (which is called as a single cell) having NaCl solution in one reservoir and NaOH solution in the other.
3. These reservoirs are connected to DC supply and the voltage of 60V is applied to the concrete specimen at both the ends for 6 hours.
5. The current passing through the concrete is determined by an LCD which is connected to the cell.
RCPT Test Formula
Q = 900 [I0 + 2I30+2I60+2I90+2I120+……+2I330+2I360]
Q = current flowing through one cell (coulombs)
I0 = initial current reading in amperes immediately after voltage is applied
It = current reading in amperes at t minutes after the voltage is applied.
For determining the accurate concrete permeability 2-3 samples are taken from same batch of concrete mix and measured as mentioned, the average value is taken as a final reading. Permeameter can have 2-3 cells with separate LCD digital meter to determine 2-3 samples at a time.
The total charge passed is determined by the above mentioned formula and used to rate the concrete according to the below criteria.
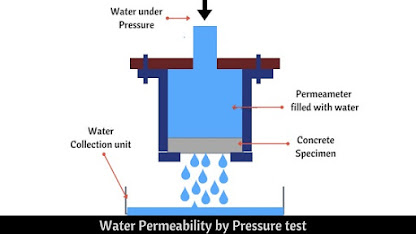
2.WATER PERMEABILITY TEST FOR CONCRETE BY PRESSURE
This test is suited and applied to the concrete having high permeability. This test is also called as Water Penetration test of concrete. This test is carried out using a disc of concrete and involves water flowing out through the disc at a steady rate.
Procedure
1. The concrete having a thickness More than 20mm is placed on Permeameter.
2. And then the Permeameter Is filled with the water.
3. To find the permeability of Concrete the water passing through the disc is collected at the water collection unit.
4. To accelerate the process, the pressure is applied to the water from the top.
Water Permeability by pressure test FormulaK = QL/ tAh
Q = discharge of water into collection unit
t = elapsed time in secs.
L = top length of concrete specimen
A = top area of concrete specimen
h = applied pressure head in m
3. SALT PONDING TEST
This test measures the resistance of concrete to chloride ion penetration. The penetration of chlorides into concrete is very severe when compared with the other deleterious substances. This bought attention to most of the researchers to find the permeability of concrete based on chlorides compared to other mechanisms.
In this test, the concrete sample is sealed on sides and the 3.0% NaCl Solution is ponded above the surface of the concrete.
Procedure for Salt Ponding test1 This test requires a large sample of concrete when compared with the other tests. 3 concrete slabs of length & breadth 300mm x 300mm and thickness 75mm are cast and cured for 14 days and kept in the drying room for 28 days with a 50% relative humidity environment before conducting the test.
2 Each concrete slab is sealed on both sides and 3% of NaCl Solution is ponded on the top surface for 90days.
3 The bottom face of the concrete slab is left exposed to the drying environment.
The specimens are maintained with a constant amount of chloride solution at top surface for 90 days.
After completion of 90 days, the specimen is sliced as a layers having thickness 12mm each which means each specimen is cut into 6 segments.
Results
If the concrete is impervious the chloride penetration in the layers is zero.
If the concrete is more permeable then chlorides may penetrate up to the second or third layer from top.
This test is used as a specification writing where you can choose the strength of concrete based on the chloride penetration. Suppose, if you want an excellent impervious concrete you may write specification as Chloride penetration up to a layer 1.
Apparatus:








No comments:
Post a Comment